-
 Using Contrastive Pairs Although many children may progress quickly through a regular articulation program, some respond better using a phonological approach. This program uses the contrastive phonological approach of Minimal Pairs. The use of Minimal Pairs is supported by evidence-based practice and has been shown to be an effective and efficient treatment for contrasting vowels or consonants. Once the ‘ch’ sound has been established in single, meaningful words, this program can be used. It will help your child hear and use the sound correctly to affect a change in meaning. Although your child is generally able to identify your ‘ch’ productions, he may use the error sounds ‘t’ or 'ts' for any ‘ch’ words. e.g. He may say ... ‘two’ when he means to say ‘chew’ ‘mats’ when he means to say ‘match’ ‘tin’ when he means to say ‘chin’ As he says the words, he may not recognise that he is using an incorrect sound. These sound errors can affect his intelligibility and will change the meaning in his connected speech.
Using Contrastive Pairs Although many children may progress quickly through a regular articulation program, some respond better using a phonological approach. This program uses the contrastive phonological approach of Minimal Pairs. The use of Minimal Pairs is supported by evidence-based practice and has been shown to be an effective and efficient treatment for contrasting vowels or consonants. Once the ‘ch’ sound has been established in single, meaningful words, this program can be used. It will help your child hear and use the sound correctly to affect a change in meaning. Although your child is generally able to identify your ‘ch’ productions, he may use the error sounds ‘t’ or 'ts' for any ‘ch’ words. e.g. He may say ... ‘two’ when he means to say ‘chew’ ‘mats’ when he means to say ‘match’ ‘tin’ when he means to say ‘chin’ As he says the words, he may not recognise that he is using an incorrect sound. These sound errors can affect his intelligibility and will change the meaning in his connected speech. -
 Wise Words indigenous materials have been devised to support parents, teachers and clinicians who may find it challenging to teach indigenous content because of concerns that they may not have the knowledge or understanding to ensure that the books, their stories and the complexity of the information is presented in a respectful and appropriate manner. With thanks to Tara Lewis who kindly edited these resources. Tara Lewis is a Speech Pathologist and member of Speech Pathology Australia's Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander Advisory Committee. Tara is an Iman woman from the Taroom country of Western Queensland. The Australian Curriculum has established Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander histories and cultures as a priority. This will ensure that Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander students are able to see themselves, their identities and their cultures reflected in the curriculum of each of the learning areas. Exposure to these and other indigenous books can build awareness of and respect for Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander histories and cultures amongst all Australian children. USING BOOKS TO ENHANCE A CHILD'S UNDERSTANDING AND INCREASE HIS/HER EXPRESSIVE LANGUAGE You can use a book to expand a child's • Vocabulary (warrior, coast, oysters, tribes, corroborees, trade, hovering) • Understanding of concepts (e.g. often, wise, great, fresh) • Ability to understand questions Bittangabee Tribe is based around important aspects of traditional Aboriginal life. The book describes the lives of an aboriginal family on the south coast of NSW. The story follows the family on their annual journey into the mountains to meet with other groups and their return to their home near the sea. Wise Words Scripts - offer clinicians, teachers and parents readily available questions designed specifically for each book. A script provides a variety of questions at each level of understanding for each page of the book. A teacher or clinician working with a group of children can tailor questions to each child's language ability. This script and other available scripts have been based on Marion Blank's Model of Classroom Language.
Wise Words indigenous materials have been devised to support parents, teachers and clinicians who may find it challenging to teach indigenous content because of concerns that they may not have the knowledge or understanding to ensure that the books, their stories and the complexity of the information is presented in a respectful and appropriate manner. With thanks to Tara Lewis who kindly edited these resources. Tara Lewis is a Speech Pathologist and member of Speech Pathology Australia's Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander Advisory Committee. Tara is an Iman woman from the Taroom country of Western Queensland. The Australian Curriculum has established Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander histories and cultures as a priority. This will ensure that Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander students are able to see themselves, their identities and their cultures reflected in the curriculum of each of the learning areas. Exposure to these and other indigenous books can build awareness of and respect for Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander histories and cultures amongst all Australian children. USING BOOKS TO ENHANCE A CHILD'S UNDERSTANDING AND INCREASE HIS/HER EXPRESSIVE LANGUAGE You can use a book to expand a child's • Vocabulary (warrior, coast, oysters, tribes, corroborees, trade, hovering) • Understanding of concepts (e.g. often, wise, great, fresh) • Ability to understand questions Bittangabee Tribe is based around important aspects of traditional Aboriginal life. The book describes the lives of an aboriginal family on the south coast of NSW. The story follows the family on their annual journey into the mountains to meet with other groups and their return to their home near the sea. Wise Words Scripts - offer clinicians, teachers and parents readily available questions designed specifically for each book. A script provides a variety of questions at each level of understanding for each page of the book. A teacher or clinician working with a group of children can tailor questions to each child's language ability. This script and other available scripts have been based on Marion Blank's Model of Classroom Language. -
 USING BOOKS TO ENHANCE A CHILD'S UNDERSTANDING AND INCREASE HIS/HER EXPRESSIVE LANGUAGE You can use a book to expand a child's • Vocabulary (seagull, beach, towel, fishing net, wave, rowing) • Understanding of concepts (wet, sandy, angry) • Ability to understand questions Wise Words Scripts - offer clinicians, teachers and parents readily available questions designed specifically for each book. A script provides a variety of questions at each level of understanding for each page of the book. A teacher or clinician working with a group of children can tailor questions to each child's language ability. This script and other available scripts have been based on Marion Blank's Model of Classroom Language. Marion Blank recognised the importance of keeping questions and statements within a child’s level of understanding. The more concrete the statement or question, the easier it will be for the child to understand. As questions become more abstract, they become harder for children to answer. The Blank Model is divided into 4 levels of questioning, moving from the concrete (easiest) at Level 1 to the abstract (most difficult) at Level 4.
USING BOOKS TO ENHANCE A CHILD'S UNDERSTANDING AND INCREASE HIS/HER EXPRESSIVE LANGUAGE You can use a book to expand a child's • Vocabulary (seagull, beach, towel, fishing net, wave, rowing) • Understanding of concepts (wet, sandy, angry) • Ability to understand questions Wise Words Scripts - offer clinicians, teachers and parents readily available questions designed specifically for each book. A script provides a variety of questions at each level of understanding for each page of the book. A teacher or clinician working with a group of children can tailor questions to each child's language ability. This script and other available scripts have been based on Marion Blank's Model of Classroom Language. Marion Blank recognised the importance of keeping questions and statements within a child’s level of understanding. The more concrete the statement or question, the easier it will be for the child to understand. As questions become more abstract, they become harder for children to answer. The Blank Model is divided into 4 levels of questioning, moving from the concrete (easiest) at Level 1 to the abstract (most difficult) at Level 4. -
 USING BOOKS TO ENHANCE A CHILD'S UNDERSTANDING AND INCREASE HIS/HER EXPRESSIVE LANGUAGE You can use a book to expand a child's • vocabulary (easel, paints, bell, singing, drawing, cubby house, chimney) • understanding of concepts (e.g. sad, prickly, up, under, heavy, mess) • ability to understand questions Wise Words Scripts - offer clinicians, teachers and parents readily available questions designed specifically for each book. A script provides a variety of questions at each level of understanding for each page of the book. A teacher or clinician working with a group of children can tailor questions to each child's language ability. This script and other available scripts have been based on Marion Blank's Model of Classroom Language. Marion Blank recognised the importance of keeping questions and statements within a child’s level of understanding. The more concrete the statement or question, the easier it will be for the child to understand. As questions become more abstract, they become harder for children to answer. The Blank Model is divided into 4 levels of questioning, moving from the concrete (easiest) at Level 1 to the abstract (most difficult) at Level 4.
USING BOOKS TO ENHANCE A CHILD'S UNDERSTANDING AND INCREASE HIS/HER EXPRESSIVE LANGUAGE You can use a book to expand a child's • vocabulary (easel, paints, bell, singing, drawing, cubby house, chimney) • understanding of concepts (e.g. sad, prickly, up, under, heavy, mess) • ability to understand questions Wise Words Scripts - offer clinicians, teachers and parents readily available questions designed specifically for each book. A script provides a variety of questions at each level of understanding for each page of the book. A teacher or clinician working with a group of children can tailor questions to each child's language ability. This script and other available scripts have been based on Marion Blank's Model of Classroom Language. Marion Blank recognised the importance of keeping questions and statements within a child’s level of understanding. The more concrete the statement or question, the easier it will be for the child to understand. As questions become more abstract, they become harder for children to answer. The Blank Model is divided into 4 levels of questioning, moving from the concrete (easiest) at Level 1 to the abstract (most difficult) at Level 4. -
 USING BOOKS TO ENHANCE A CHILD'S UNDERSTANDING AND INCREASE HIS/HER EXPRESSIVE LANGUAGE You can use a book to expand a child's • Vocabulary (basket, trowel, snail, finding, bench, sack, core) • Understanding of concepts (under, hungry, angry, behind, crunchy, finished, broken) • Ability to understand questions Wise Words Scripts - offer clinicians, teachers and parents readily available questions designed specifically for each book. A script provides a variety of questions at each level of understanding for each page of the book. A teacher or clinician working with a group of children can tailor questions to each child's language ability. This script and other available scripts have been based on Marion Blank's Model of Classroom Language. Marion Blank recognised the importance of keeping questions and statements within a child’s level of understanding. The more concrete the statement or question, the easier it will be for the child to understand. As questions become more abstract, they become harder for children to answer. The Blank Model is divided into 4 levels of questioning, moving from the concrete (easiest) at Level 1 to the abstract (most difficult) at Level 4.
USING BOOKS TO ENHANCE A CHILD'S UNDERSTANDING AND INCREASE HIS/HER EXPRESSIVE LANGUAGE You can use a book to expand a child's • Vocabulary (basket, trowel, snail, finding, bench, sack, core) • Understanding of concepts (under, hungry, angry, behind, crunchy, finished, broken) • Ability to understand questions Wise Words Scripts - offer clinicians, teachers and parents readily available questions designed specifically for each book. A script provides a variety of questions at each level of understanding for each page of the book. A teacher or clinician working with a group of children can tailor questions to each child's language ability. This script and other available scripts have been based on Marion Blank's Model of Classroom Language. Marion Blank recognised the importance of keeping questions and statements within a child’s level of understanding. The more concrete the statement or question, the easier it will be for the child to understand. As questions become more abstract, they become harder for children to answer. The Blank Model is divided into 4 levels of questioning, moving from the concrete (easiest) at Level 1 to the abstract (most difficult) at Level 4. -

Level 2
Naming and grouping an object within a category “Find something that is a food." "Hamburger - which group does this belong in?” “Is this in the furniture group?” “Which group are you collecting?” “What belongs in your group?” Attending to two characteristics “Find something that gives milk and eats grass.” “Find something that is an animal and has a long neck.” “Find the things that grow and we can eat.” This program provides opportunities to teach the concept of semantic groups/grouping of objects. - Children learn new words more easily if they fully understand the meaning of a word. Therefore, it is important for the child to understand the semantic features and how a word can be categorised. Initially he is required to group non-identical but almost the same objects. The semantic features and similarities of each object are discussed and sorted using the ‘Group Board’. This activity gives the child a number of links to the non-identical objects (cars) or group name (e.g. fruit, transport). Discussing and comparing the semantic features of objects provides a ‘mapping’ experience to ensure that the word is learnt more successfully. This program can also be used to target and identify similarities or differences while providing the child with additional information to use inductive reasoning. Research indicates that we store and retrieve words more easily if they have been organised into ‘collections’. Two important ways that we can organise words are by ... • Function - what we do with something (eat cake), what we use it for (cut with - scissors) or what it does (a bird flies). • Semantic Class - A ‘word family’ includes groups such as food (cake, eggs, bread, cheese), wild animals (zebra, giraffe, lion, monkey), furniture (chair, bed, table, shelves). This program targets the classification of objects into Semantic Classes whilst providing the child with multiple links which they can use to retrieve the words at a later time. Initially the child is presented with objects which are similar (all balls) but not identical (e.g. football, tennis ball, bowling ball, basketball). Once a child is able to group non-identical objects into groups, the Semantic Class cards and boards are presented (e.g. food, furniture, clothes, farm animals). Contents - 34 pages including instructions. -

Level 3 (& Level 4)
Selecting an Object or Set of Objects by Exclusion Level 3 “Tell me something else that ...” “Tell me something different that ..." "Show me the things that aren’t ...” “Point to the things that don’t ...” “Find the things that the boy can’t ...” Reasoning & Problem Solving Level 4 “Why is a ... made of ...?" "What should he do if ...?" "Why wouldn't ...?" "What could you use to ...?" "What could you ... if ...?" This program targets Level 3 questions and statements. At this level of understanding, your child will need to look beyond the material in front of him. He will be required to evaluate and reorder the information. A typical skill in this category is the ability to exclude material. Your child will need to follow directions which may use the words ‘not, don’t, can’t, something else, other than’. The activities in this program have been designed specifically to help your child recognise alternatives. A number of Level 4 questions have been included in this program. These tasks will prove useful for those children who are working towards a more abstract type of question. Questions at this level include Why should ...? Why shouldn’t ...? Why can ...? Why can’t ...? What could ...? How can we tell ...? At this level of understanding, your child will need to look beyond the material in front of him/her and will then be required to evaluate and reorder the information. A typical skill in this category is the ability to exclude material. Your child will need to follow directions which may include the words ‘not, don’t, can’t, something else, other than’. The activities in this program have been designed specifically to help your child recognise alternatives. Example of a Level 3 Activity 1. “A cow is a farm animal. “Tell me something different that is a farm animal.” Your child is given the following possible answers: A camel - An animal but not a farm animal. A pig - The correct answer. This is an alternative farm animal. A farm - The place where farm animals are found. A lion - An animal but not a farm animal. 2. “Which animals don’t belong on the farm?” - “Camel, lion” Example of a Level 4 Activity 1.“Mum fills the kettle with water. How can we tell that the kettle is boiling?" 2. “Frogs can jump. Why can’t snails jump? -
Sale!
 10% Discount Applied to Total Package (See individual programs for details and examples.) The Total Articulation Package includes 13 Articulation Programs. This consists of 6 consonant and 4 vowel programs. Consonant - 'L' Consonant - 'th' voiceless Consonant - 'th' voiced Consonant - 'r' Consonant - 's' Consonant - Minimal Pairs - 'k' vs 't' Consonant - Minimal Pairs - 'sh' vs 's' Consonant - Minimal Pairs - 'ch' vs 't' Vowel - 'ir' Vowel - 'air' Vowel - 'eh' Vowel - Minimal Pairs - 'ir' vs 'or' Wise Words Articulation Programs support clinicians, teachers and parents to establish 'new' (correct) sounds into their child's speech. Each program supplies detailed instructions for every task and game. The instructions have been written in a clear manner for a non-professional to follow. Numerous games are provided. These games have been designed to be fun and interactive and will ensure that the child remains engaged and compliant. Playing the games will help the child to generalise the ‘new’ sound into their everyday speech.
10% Discount Applied to Total Package (See individual programs for details and examples.) The Total Articulation Package includes 13 Articulation Programs. This consists of 6 consonant and 4 vowel programs. Consonant - 'L' Consonant - 'th' voiceless Consonant - 'th' voiced Consonant - 'r' Consonant - 's' Consonant - Minimal Pairs - 'k' vs 't' Consonant - Minimal Pairs - 'sh' vs 's' Consonant - Minimal Pairs - 'ch' vs 't' Vowel - 'ir' Vowel - 'air' Vowel - 'eh' Vowel - Minimal Pairs - 'ir' vs 'or' Wise Words Articulation Programs support clinicians, teachers and parents to establish 'new' (correct) sounds into their child's speech. Each program supplies detailed instructions for every task and game. The instructions have been written in a clear manner for a non-professional to follow. Numerous games are provided. These games have been designed to be fun and interactive and will ensure that the child remains engaged and compliant. Playing the games will help the child to generalise the ‘new’ sound into their everyday speech. -
 Wise Words Articulation Programs support clinicians, teachers and parents to establish 'new' (correct) sounds into their child's speech. Each program supplies detailed instructions for every task and game. The instructions have been written in a clear manner for a non-professional to follow. Numerous games are provided. These games have been designed to be fun and interactive and will ensure that the child remains engaged and compliant. Playing the games will help the child to generalise the ‘new’ sound into their everyday speech.
Wise Words Articulation Programs support clinicians, teachers and parents to establish 'new' (correct) sounds into their child's speech. Each program supplies detailed instructions for every task and game. The instructions have been written in a clear manner for a non-professional to follow. Numerous games are provided. These games have been designed to be fun and interactive and will ensure that the child remains engaged and compliant. Playing the games will help the child to generalise the ‘new’ sound into their everyday speech. -
 Wise Words Articulation Programs - support clinicians, teachers and parents to establish 'new' (correct) sounds into their child's speech. Each program supplies detailed instructions for every task and game. The instructions have been written in a clear manner for a non-professional to follow. Numerous games are provided. These games have been designed to be fun and interactive and will ensure that the child remains engaged and compliant. Playing the games will help the child to generalise the ‘new’ sound into their everyday speech.
Wise Words Articulation Programs - support clinicians, teachers and parents to establish 'new' (correct) sounds into their child's speech. Each program supplies detailed instructions for every task and game. The instructions have been written in a clear manner for a non-professional to follow. Numerous games are provided. These games have been designed to be fun and interactive and will ensure that the child remains engaged and compliant. Playing the games will help the child to generalise the ‘new’ sound into their everyday speech. -
 USING BOOKS TO ENHANCE A CHILD'S UNDERSTANDING AND INCREASE HIS/HER EXPRESSIVE LANGUAGE You can use a book to expand a child's • vocabulary (invitation, balloons, riding, dancing, horse) • understanding of concepts (e.g. inside, under, surprised, all) • ability to understand questions Wise Words Scripts - offer clinicians, teachers and parents readily available questions designed specifically for each book. A script provides a variety of questions at each level of understanding for each page of the book. A teacher or clinician working with a group of children can tailor questions to each child's language ability. This script and other available scripts have been based on Marion Blank's Model of Classroom Language. Marion Blank recognised the importance of keeping questions and statements within a child’s level of understanding. The more concrete the statement or question, the easier it will be for the child to understand. As questions become more abstract, they become harder for children to answer. The Blank Model is divided into 4 levels of questioning, moving from the concrete (easiest) at Level 1 to the abstract (most difficult) at Level 4.
USING BOOKS TO ENHANCE A CHILD'S UNDERSTANDING AND INCREASE HIS/HER EXPRESSIVE LANGUAGE You can use a book to expand a child's • vocabulary (invitation, balloons, riding, dancing, horse) • understanding of concepts (e.g. inside, under, surprised, all) • ability to understand questions Wise Words Scripts - offer clinicians, teachers and parents readily available questions designed specifically for each book. A script provides a variety of questions at each level of understanding for each page of the book. A teacher or clinician working with a group of children can tailor questions to each child's language ability. This script and other available scripts have been based on Marion Blank's Model of Classroom Language. Marion Blank recognised the importance of keeping questions and statements within a child’s level of understanding. The more concrete the statement or question, the easier it will be for the child to understand. As questions become more abstract, they become harder for children to answer. The Blank Model is divided into 4 levels of questioning, moving from the concrete (easiest) at Level 1 to the abstract (most difficult) at Level 4. -
 USING BOOKS TO ENHANCE A CHILD'S UNDERSTANDING AND INCREASE HIS/HER EXPRESSIVE LANGUAGE You can use a book to expand a child's • Vocabulary (snowman, shivered, smile, melted, winter, wind) • Understanding of concepts (warm, cold, new, hot, freezing) • Ability to understand questions Wise Words Scripts - offer clinicians, teachers and parents readily available questions designed specifically for each book. A script provides a variety of questions at each level of understanding for each page of the book. A teacher or clinician working with a group of children can tailor questions to each child's language ability. This script and other available scripts have been based on Marion Blank's Model of Classroom Language. Marion Blank recognised the importance of keeping questions and statements within a child’s level of understanding. The more concrete the statement or question, the easier it will be for the child to understand. As questions become more abstract, they become harder for children to answer. The Blank Model is divided into 4 levels of questioning, moving from the concrete (easiest) at Level 1 to the abstract (most difficult) at Level 4.
USING BOOKS TO ENHANCE A CHILD'S UNDERSTANDING AND INCREASE HIS/HER EXPRESSIVE LANGUAGE You can use a book to expand a child's • Vocabulary (snowman, shivered, smile, melted, winter, wind) • Understanding of concepts (warm, cold, new, hot, freezing) • Ability to understand questions Wise Words Scripts - offer clinicians, teachers and parents readily available questions designed specifically for each book. A script provides a variety of questions at each level of understanding for each page of the book. A teacher or clinician working with a group of children can tailor questions to each child's language ability. This script and other available scripts have been based on Marion Blank's Model of Classroom Language. Marion Blank recognised the importance of keeping questions and statements within a child’s level of understanding. The more concrete the statement or question, the easier it will be for the child to understand. As questions become more abstract, they become harder for children to answer. The Blank Model is divided into 4 levels of questioning, moving from the concrete (easiest) at Level 1 to the abstract (most difficult) at Level 4. -
 USING BOOKS TO ENHANCE A CHILD’S UNDERSTANDING AND INCREASE HIS/HER EXPRESSIVE LANGUAGE You can use a book to expand a child’s • vocabulary (frolics, jig, grumble, charged, larder, jug) • understanding of concepts (e.g. enormous, wise, curious, tiny, out) • ability to understand questions Wise Words Scripts – offer clinicians, teachers and parents readily available questions designed specifically for each book. A script provides a variety of questions at each level of understanding for each page of the book. A teacher or clinician working with a group of children can tailor questions to each child’s language ability. This script and other available scripts have been based on Marion Blank’s Model of Classroom Language. Marion Blank recognised the importance of keeping questions and statements within a child’s level of understanding. The more concrete the statement or question, the easier it will be for the child to understand. As questions become more abstract, they become harder for children to answer. The Blank Model is divided into 4 levels of questioning, moving from the concrete (easiest) at Level 1 to the abstract (most difficult) at Level 4. All Wise Words Programs are sent as a download unless otherwise specified. To ship a USB, please add either Australian (A$20) or International (A$55) shipping to shopping cart.
USING BOOKS TO ENHANCE A CHILD’S UNDERSTANDING AND INCREASE HIS/HER EXPRESSIVE LANGUAGE You can use a book to expand a child’s • vocabulary (frolics, jig, grumble, charged, larder, jug) • understanding of concepts (e.g. enormous, wise, curious, tiny, out) • ability to understand questions Wise Words Scripts – offer clinicians, teachers and parents readily available questions designed specifically for each book. A script provides a variety of questions at each level of understanding for each page of the book. A teacher or clinician working with a group of children can tailor questions to each child’s language ability. This script and other available scripts have been based on Marion Blank’s Model of Classroom Language. Marion Blank recognised the importance of keeping questions and statements within a child’s level of understanding. The more concrete the statement or question, the easier it will be for the child to understand. As questions become more abstract, they become harder for children to answer. The Blank Model is divided into 4 levels of questioning, moving from the concrete (easiest) at Level 1 to the abstract (most difficult) at Level 4. All Wise Words Programs are sent as a download unless otherwise specified. To ship a USB, please add either Australian (A$20) or International (A$55) shipping to shopping cart. -
 USING BOOKS TO ENHANCE A CHILD'S UNDERSTANDING AND INCREASE HIS/HER EXPRESSIVE LANGUAGE You can use a book to expand a child's • vocabulary (grandparents, shovel, garden fork, spray, eggs, visiting, picking) • understanding of concepts (e..g wet, hidden, broken, hot, comfortable) • ability to understand questions Wise Words Scripts - offer clinicians, teachers and parents readily available questions designed specifically for each book. A script provides a variety of questions at each level of understanding for each page of the book. A teacher or clinician working with a group of children can tailor questions to each child's language ability. This script and other available scripts have been based on Marion Blank's Model of Classroom Language. Marion Blank recognised the importance of keeping questions and statements within a child’s level of understanding. The more concrete the statement or question, the easier it will be for the child to understand. As questions become more abstract, they become harder for children to answer. The Blank Model is divided into 4 levels of questioning, moving from the concrete (easiest) at Level 1 to the abstract (most difficult) at Level 4.
USING BOOKS TO ENHANCE A CHILD'S UNDERSTANDING AND INCREASE HIS/HER EXPRESSIVE LANGUAGE You can use a book to expand a child's • vocabulary (grandparents, shovel, garden fork, spray, eggs, visiting, picking) • understanding of concepts (e..g wet, hidden, broken, hot, comfortable) • ability to understand questions Wise Words Scripts - offer clinicians, teachers and parents readily available questions designed specifically for each book. A script provides a variety of questions at each level of understanding for each page of the book. A teacher or clinician working with a group of children can tailor questions to each child's language ability. This script and other available scripts have been based on Marion Blank's Model of Classroom Language. Marion Blank recognised the importance of keeping questions and statements within a child’s level of understanding. The more concrete the statement or question, the easier it will be for the child to understand. As questions become more abstract, they become harder for children to answer. The Blank Model is divided into 4 levels of questioning, moving from the concrete (easiest) at Level 1 to the abstract (most difficult) at Level 4. -
Level 4
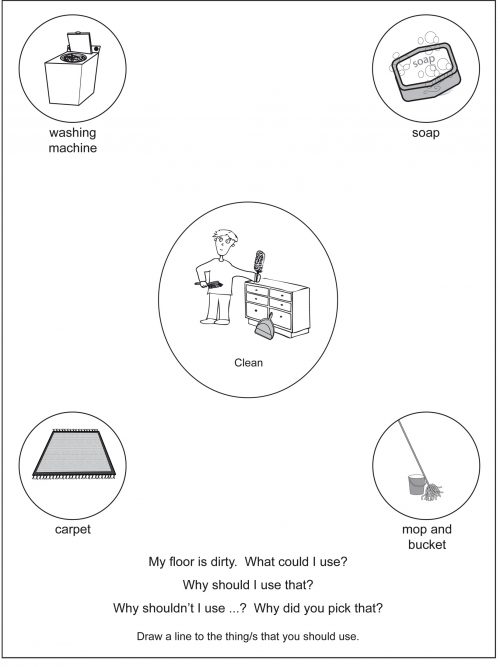
Selecting the Means to a Goal Level 4 “What should I use to ...?” “What could I do to ...?” “What could he wear if ...?” Explaining the Means to a Goal Level 4 “Why should she use...?” “Why shouldn’t she use ..?” “Why did you pick that one?” The activities presented in this Level 4 program reflect more complex verbal problems. These activities will require your child to reason about things that may, might, could or would happen. Your will need to go beyond what can be immediately seen or perceived. He/she will need to reflect on previously gained information and use this information to solve the problem. The large circle in the middle of the page contains the “problem” which your child will need to solve. This picture will set the scene for your child but it will not give your child the answer to the question. Possible solutions to each problem are located in the four smaller circles which are placed in each corner of the page. Some solutions have been chosen in order to deliberately challenge your child. For your child to offer the correct solution they will have had to completely understand the statement and understand the question. Example of a problem: This problem is related to cleaning the floor.The following solutions are offered: A washing machine - this is something used for cleaning clothes. Soap - again something for cleaning. A carpet - something that is found on the floor. A mop and bucket - the correct answer for cleaning the floor. -
Level 3
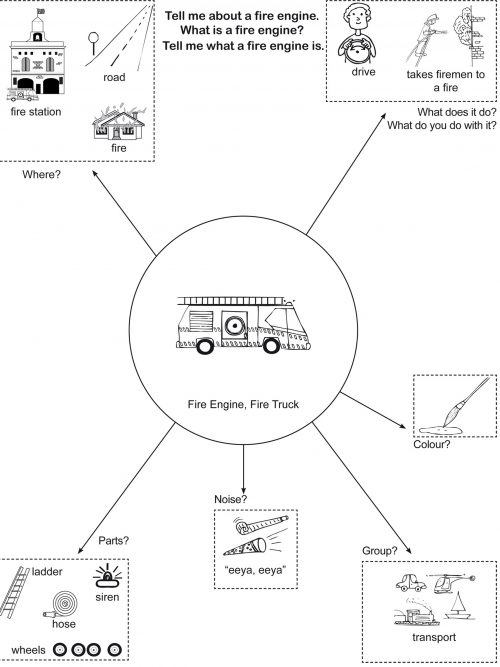
Defining Words Level 3 “What is a ...?” “Tell me what a ... is.” “Tell me what ... are.” Mind Maps - will help your child to- Talk about and describe an object
- Give 'news'
- Expand his/her vocabulary
- Find the right word
- Increase his/her descriptive language
- Answer questions
- Ask questions
- Where do you find it?
- What can you do with it?
- What shape is it?
- What colour is it?
- What group (semantic class) does it belong in?
- What parts does it have? (Labelling the parts of objects greatly increases a child's vocabulary. For example - yolk, white, shell)
- How does it feel (when touched)?
- When your child becomes competent with the specific prompts, a generic mind map is provided.
-
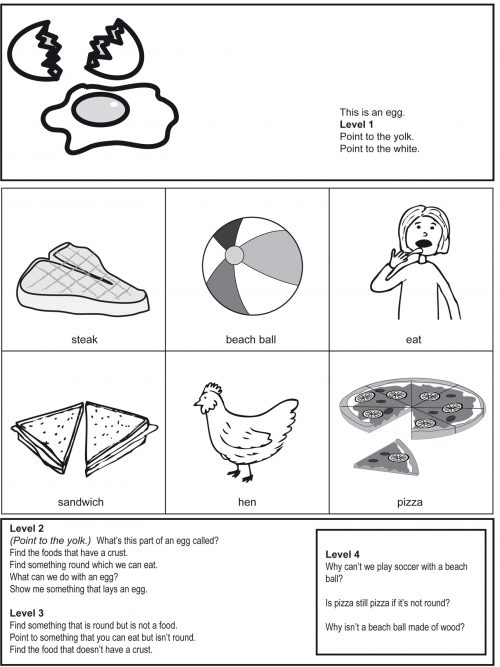
Identifying Parts of a Whole and Exclusions Level 2 - 4
Attending to Two Characteristics Naming the Parts of Objects Identifying an Object by its Function Level 2 “Find something that is round that we can eat.” “What is this part of a ... called?” “What do we use this for?” Selecting an Object by Exclusion Selecting a Set of Objects by Exclusion Level 3 “Find all the ones that are not animals." "Tell me something that is not big." “Show me something that can jump but is not a horse." Reasoning and Problem Solving Level 4 “If a bicycle wheel were square would it still be a wheel?” “Why are gumboots made of rubber?” “What will happen if ...?” "Why is a raincoat called a raincoat?" The first part of this program has been designed to help your child recognise and name parts of objects and respond to questions which focus on the object's properties and functions. (eg Selecting an object according to two characteristics – “Find the one that has an engine and wings.”) The second part of this program targets exclusion. This requires your child to overcome the urge to respond to a key word or salient perceptual material. (eg “Point to something that you can eat but isn’t round. Find something that flies in the sky but doesn't have wings.”) The final part of this program represents complex verbal problems that require a child to reason about what may, might, could or would happen to material/objects under specific circumstances. Your child will need to problem solve and formulate solutions using logic and past knowledge. Although the question may relate to an object pictured on the page, the solution to the question is not present. Examples of tasks/activities Level 2 Find something round which we can eat. What's this part of a helicopter called? Level 3 Point to something that you can eat but isn't round. Point to something that is a boat but doesn't have sails. Level 4 Why isn't a beach ball made of wood? Would a soccer ball still be a soccer ball if it were an oval shape? -

Level 2
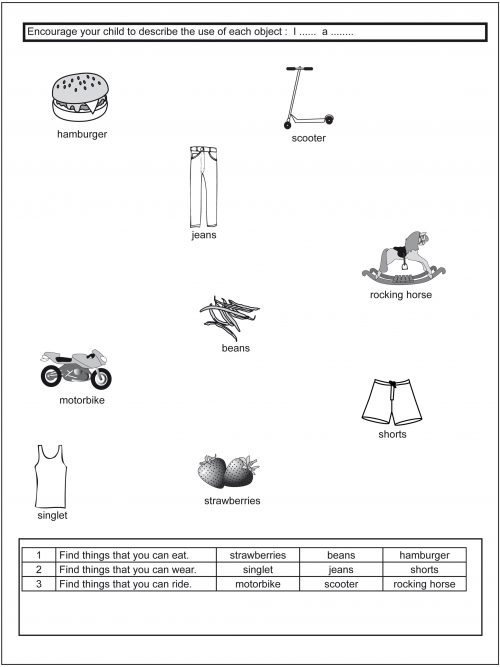
Naming the Functions of Objects Level 2 “What do we do with this?” “What is a ... for?” “What do we use a ... for?” Completing a Sentence Level 2 “You finish what I say .. " "I kick a ...” “I eat ...” “... is for eating” These worksheets are targeted at Level 2. The activities will help your child understand the function of objects, what objects are used for and what we do with them. Research indicates that we store and retrieve words more easily if they have been organised into “collections”. Classifying is an important skill for a child to learn. Understanding the function of objects is generally the first characteristic that a child attaches to an object. Your child will quickly realise that juice is for drinking and that a bed is for sleeping in. This program ensures that your child will be able to:- Select objects according to their function.
- Sort objects with similar functions.
- Name the functions of objects.
- Identify the odd one out by recognising the object’s function.