-
 This assessment tool is modeled on the Blank’s Model of Classroom Language Blank, Rose & Berlin 1978 The Wise Words Screening Advantage offers an assessment tool which is quick and easy for clinicians and teachers to administer. Ten colour pictures provide the stimulus for the questions and instructions. The questions/instructions have been designed to represent all four levels of Blank’s model and offer two questions/instructions at each level for each picture presented. This screening tool can be used to plan goals for children and will monitor the child’s progress over time. Contents - The questions/instructions have been designed to represent all four levels of Blank’s model and offer two questions/instructions at each level for each picture presented. The test form provides space beneath the prompts/questions for the clinician/teacher to transcribe the child’s response. A comprehensive table is available to allow more detailed analysis of the child's responses. The question types have been arranged into two sets, (either highlighted or non-highlighted) in order to provide the option of retesting the child without compromising the outcome. Each set ensures that the results reflect the child’s functional level of understanding. On completion of the screener, the clinician or teacher enters the raw score of the number of questions asked at each level and the number of correct responses. The number correct at each level is then calculated as a percentage.
This assessment tool is modeled on the Blank’s Model of Classroom Language Blank, Rose & Berlin 1978 The Wise Words Screening Advantage offers an assessment tool which is quick and easy for clinicians and teachers to administer. Ten colour pictures provide the stimulus for the questions and instructions. The questions/instructions have been designed to represent all four levels of Blank’s model and offer two questions/instructions at each level for each picture presented. This screening tool can be used to plan goals for children and will monitor the child’s progress over time. Contents - The questions/instructions have been designed to represent all four levels of Blank’s model and offer two questions/instructions at each level for each picture presented. The test form provides space beneath the prompts/questions for the clinician/teacher to transcribe the child’s response. A comprehensive table is available to allow more detailed analysis of the child's responses. The question types have been arranged into two sets, (either highlighted or non-highlighted) in order to provide the option of retesting the child without compromising the outcome. Each set ensures that the results reflect the child’s functional level of understanding. On completion of the screener, the clinician or teacher enters the raw score of the number of questions asked at each level and the number of correct responses. The number correct at each level is then calculated as a percentage. -
Sale!
 10% Discount Applied to Total Package (See individual programs for details and examples.) The Total Language Package includes both assessment tools and ALL programs at all 4 levels of understanding. Assessments The Wise Words Screening Tool The Wise Words Screening Advantage Level 1 Matching Objects Level 2 Functions Lotto Fish for Functions Naming Functions Sorting Functions Matching Functions Functions Board Games Semantic Naming Semantic Sorting Semantic Lotto Semantic Matching Semantic Families Semantic Board Games Two Characteristics Barrier games Level 3 Identifying Parts of a Whole and Exclusions (Levels 2 - 4) Identifying Similarities and Differences (Levels 2 - 3) Word Definitions Mind Map 1 Word Definitions Mind Map 2 Word Definitions Mind Map 3 What Will Happen Next? Selecting an Alternative Negatives and Exclusions Explaining Similarities Identifying Objects Used Together Level 4 Explaining the Logic of Compound Words Explaining an Inference Justifying a Decision Based on Characteristics Selecting the Means to a Goal Selecting a Tool Predicting Changes in Position Explaining the Reason for an Action The Wise Words Screening Tool provides range of questions/instructions representing all four levels of Blank’s model. It offers two questions/instructions at each level for each picture presented. Space is provided beneath these questions for the clinician/teacher to transcribe the child’s response. This simple screening tool can be used to plan goals for children and will monitor a child’s progress over time. The Wise Words Screening Advantage offers an assessment tool which can be administered quickly. The provided tables enable a teacher or clinician to analyse responses, devise goals and track a child’s progress over time. The screener consists of 10 colour stimulus pictures with a range of questions/instructions representing all four levels of Blank’s model. All (twenty nine) Wise Words Language programs are included in this package. These programs have been designed to support a child's language development from the early, concrete language of a younger child to the older child where the perceptual language distance has increased significantly and where language is used to problem solve and reason about materials and experiences. The Blank's levels are fluid and the Wise Words Programs assist a child to work through each level to a higher level of understanding. Each program can stand alone. There are a number of different programs available at Levels 2 - 4 to ensure firm understanding and assist in generalisation. The instructions for the programs have been written for a lay person and give detailed information on how to use the program. All programs are printed in black and white to ensure fast, cost effective printing.
10% Discount Applied to Total Package (See individual programs for details and examples.) The Total Language Package includes both assessment tools and ALL programs at all 4 levels of understanding. Assessments The Wise Words Screening Tool The Wise Words Screening Advantage Level 1 Matching Objects Level 2 Functions Lotto Fish for Functions Naming Functions Sorting Functions Matching Functions Functions Board Games Semantic Naming Semantic Sorting Semantic Lotto Semantic Matching Semantic Families Semantic Board Games Two Characteristics Barrier games Level 3 Identifying Parts of a Whole and Exclusions (Levels 2 - 4) Identifying Similarities and Differences (Levels 2 - 3) Word Definitions Mind Map 1 Word Definitions Mind Map 2 Word Definitions Mind Map 3 What Will Happen Next? Selecting an Alternative Negatives and Exclusions Explaining Similarities Identifying Objects Used Together Level 4 Explaining the Logic of Compound Words Explaining an Inference Justifying a Decision Based on Characteristics Selecting the Means to a Goal Selecting a Tool Predicting Changes in Position Explaining the Reason for an Action The Wise Words Screening Tool provides range of questions/instructions representing all four levels of Blank’s model. It offers two questions/instructions at each level for each picture presented. Space is provided beneath these questions for the clinician/teacher to transcribe the child’s response. This simple screening tool can be used to plan goals for children and will monitor a child’s progress over time. The Wise Words Screening Advantage offers an assessment tool which can be administered quickly. The provided tables enable a teacher or clinician to analyse responses, devise goals and track a child’s progress over time. The screener consists of 10 colour stimulus pictures with a range of questions/instructions representing all four levels of Blank’s model. All (twenty nine) Wise Words Language programs are included in this package. These programs have been designed to support a child's language development from the early, concrete language of a younger child to the older child where the perceptual language distance has increased significantly and where language is used to problem solve and reason about materials and experiences. The Blank's levels are fluid and the Wise Words Programs assist a child to work through each level to a higher level of understanding. Each program can stand alone. There are a number of different programs available at Levels 2 - 4 to ensure firm understanding and assist in generalisation. The instructions for the programs have been written for a lay person and give detailed information on how to use the program. All programs are printed in black and white to ensure fast, cost effective printing. -
 USING BOOKS TO ENHANCE A CHILD'S UNDERSTANDING AND INCREASE HIS/HER EXPRESSIVE LANGUAGE You can use a book to expand a child's • vocabulary (plait, beast, fluttered, cloak, cauldron, bog) • understanding of concepts (storm, tall, scary, clean, politely) • ability to understand questions Wise Words Scripts - offer clinicians, teachers and parents readily available questions designed specifically for each book. A script provides a variety of questions at each level of understanding for each page of the book. A teacher or clinician working with a group of children can tailor questions to each child's language ability. This script and other available scripts have been based on Marion Blank's Model of Classroom Language. Marion Blank recognised the importance of keeping questions and statements within a child’s level of understanding. The more concrete the statement or question, the easier it will be for the child to understand. As questions become more abstract, they become harder for children to answer. The Blank Model is divided into 4 levels of questioning, moving from the concrete (easiest) at Level 1 to the abstract (most difficult) at Level 4.
USING BOOKS TO ENHANCE A CHILD'S UNDERSTANDING AND INCREASE HIS/HER EXPRESSIVE LANGUAGE You can use a book to expand a child's • vocabulary (plait, beast, fluttered, cloak, cauldron, bog) • understanding of concepts (storm, tall, scary, clean, politely) • ability to understand questions Wise Words Scripts - offer clinicians, teachers and parents readily available questions designed specifically for each book. A script provides a variety of questions at each level of understanding for each page of the book. A teacher or clinician working with a group of children can tailor questions to each child's language ability. This script and other available scripts have been based on Marion Blank's Model of Classroom Language. Marion Blank recognised the importance of keeping questions and statements within a child’s level of understanding. The more concrete the statement or question, the easier it will be for the child to understand. As questions become more abstract, they become harder for children to answer. The Blank Model is divided into 4 levels of questioning, moving from the concrete (easiest) at Level 1 to the abstract (most difficult) at Level 4. -
 USING BOOKS TO ENHANCE A CHILD'S UNDERSTANDING AND INCREASE HIS/HER EXPRESSIVE LANGUAGE You can use a book to expand a child's • vocabulary (stream, feast, log pile, poisonous, rumble, scrambled) • understanding of concepts (e.g. quick, favourite, good, dark, scariest) • ability to understand questions Wise Words Scripts - offer clinicians, teachers and parents readily available questions designed specifically for each book. A script provides a variety of questions at each level of understanding for each page of the book. A teacher or clinician working with a group of children can tailor questions to each child's language ability. This script and other available scripts have been based on Marion Blank's Model of Classroom Language. Marion Blank recognised the importance of keeping questions and statements within a child’s level of understanding. The more concrete the statement or question, the easier it will be for the child to understand. As questions become more abstract, they become harder for children to answer. The Blank Model is divided into 4 levels of questioning, moving from the concrete (easiest) at Level 1 to the abstract (most difficult) at Level 4.
USING BOOKS TO ENHANCE A CHILD'S UNDERSTANDING AND INCREASE HIS/HER EXPRESSIVE LANGUAGE You can use a book to expand a child's • vocabulary (stream, feast, log pile, poisonous, rumble, scrambled) • understanding of concepts (e.g. quick, favourite, good, dark, scariest) • ability to understand questions Wise Words Scripts - offer clinicians, teachers and parents readily available questions designed specifically for each book. A script provides a variety of questions at each level of understanding for each page of the book. A teacher or clinician working with a group of children can tailor questions to each child's language ability. This script and other available scripts have been based on Marion Blank's Model of Classroom Language. Marion Blank recognised the importance of keeping questions and statements within a child’s level of understanding. The more concrete the statement or question, the easier it will be for the child to understand. As questions become more abstract, they become harder for children to answer. The Blank Model is divided into 4 levels of questioning, moving from the concrete (easiest) at Level 1 to the abstract (most difficult) at Level 4. -
 Wise Words indigenous materials have been devised to support parents, teachers and clinicians who may find it challenging to teach indigenous content because of concerns that they may not have the knowledge or understanding to ensure that the books, their stories and the complexity of the information is presented in a respectful and appropriate manner. With thanks to Tara Lewis who kindly edited these resources. Tara Lewis is a Speech Pathologist and member of Speech Pathology Australia's Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander Advisory Committee. Tara is an Iman woman from the Taroom country of Western Queensland. The Australian Curriculum has established Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander histories and cultures as a priority. This will ensure that Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander students are able to see themselves, their identities and their cultures reflected in the curriculum of each of the learning areas. Exposure to these and other indigenous books can build awareness of and respect for Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander histories and cultures amongst all Australian children. USING BOOKS TO ENHANCE A CHILD'S UNDERSTANDING AND INCREASE HIS/HER EXPRESSIVE LANGUAGE You can use a book to expand a child's • Vocabulary (gum tree, eucalyptus, ambled, burrow, stream) • Understanding of concepts (e.g. busy, quietly, frightened, impatiently, huffy) • Ability to understand questions A Home for Bilby describes the Australian bush and the habitats of the animals that live there. As the animals describe their daily lives and habitats, they develop sympathy for Bilby and help him find a home which is just right for him. Wise Words Scripts - offer clinicians, teachers and parents readily available questions designed specifically for each book. A script provides a variety of questions at each level of understanding for each page of the book. A teacher or clinician working with a group of children can tailor questions to each child's language ability. This script and other available scripts have been based on Marion Blank's Model of Classroom Language.
Wise Words indigenous materials have been devised to support parents, teachers and clinicians who may find it challenging to teach indigenous content because of concerns that they may not have the knowledge or understanding to ensure that the books, their stories and the complexity of the information is presented in a respectful and appropriate manner. With thanks to Tara Lewis who kindly edited these resources. Tara Lewis is a Speech Pathologist and member of Speech Pathology Australia's Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander Advisory Committee. Tara is an Iman woman from the Taroom country of Western Queensland. The Australian Curriculum has established Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander histories and cultures as a priority. This will ensure that Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander students are able to see themselves, their identities and their cultures reflected in the curriculum of each of the learning areas. Exposure to these and other indigenous books can build awareness of and respect for Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander histories and cultures amongst all Australian children. USING BOOKS TO ENHANCE A CHILD'S UNDERSTANDING AND INCREASE HIS/HER EXPRESSIVE LANGUAGE You can use a book to expand a child's • Vocabulary (gum tree, eucalyptus, ambled, burrow, stream) • Understanding of concepts (e.g. busy, quietly, frightened, impatiently, huffy) • Ability to understand questions A Home for Bilby describes the Australian bush and the habitats of the animals that live there. As the animals describe their daily lives and habitats, they develop sympathy for Bilby and help him find a home which is just right for him. Wise Words Scripts - offer clinicians, teachers and parents readily available questions designed specifically for each book. A script provides a variety of questions at each level of understanding for each page of the book. A teacher or clinician working with a group of children can tailor questions to each child's language ability. This script and other available scripts have been based on Marion Blank's Model of Classroom Language. -
 (‘Spot Bakes a Cake’ by Eric Hill) A Screening tool based on the Blank's Model of Classroom Language This simple test, based on the Blank’s Model of Classroom Language (Blank, Rose & Berlin 1978), offers teachers and clinicians a screening tool which is quick and easy to administer. The pictures in the book ‘Spot Bakes a Cake’ provide the stimulus for the questions. Contents - A range of questions/instructions represent all four levels of Blank’s model. This screener offers two questions/instructions at each level for each picture presented. Space is provided beneath these questions for the clinician/teacher to transcribe the child’s response. It is not necessary to ask every question and many children would be unable to sustain interest if all questions were posed. The questions have been arranged into two sets to ensure that a variety of question types is included in each set. For screening purposes, one set is highlighted on the test form. It is recommended that you ask only one set of questions as each set of questions will ensure that you gain a functional picture of a child’s level of understanding. This simple screening tool can be used to plan goals for children and will monitor a child’s progress over time. On completion of the screener, the clinician or teacher enters the raw score of the number of questions asked at each level and the number of correct responses. The number correct at each level is then calculated as a percentage. The criteria referred to in this screener are provided by Marion Blank et al in the following publications ... • The Language of Learning: The Preschool Years - Blank, Rose & Berlin,1978 • Preschool Language Assessment Instrument (PLAI) - Blank, Rose, Berlin, Laura, 1978 Examples of questions provided in the screener: Level 3 Selecting an object by excluding a specific object Find something that is red but is not an apple. Selecting an alternative Sally is holding a cloth. Tell me something else that she could use to pick up the cake. Describing an event that might happen Sally is reading her shopping list. What will she do next? Defining a word What is an egg? Tell me what an egg is. Identifying Similarities This is a card and this is an envelope. How are these things the same? Generalising about a set of events (Point to the bones scattered on the table.) What happened to these bones? Citing an example by excluding a set of objects Tell me something that you can’t wear.
(‘Spot Bakes a Cake’ by Eric Hill) A Screening tool based on the Blank's Model of Classroom Language This simple test, based on the Blank’s Model of Classroom Language (Blank, Rose & Berlin 1978), offers teachers and clinicians a screening tool which is quick and easy to administer. The pictures in the book ‘Spot Bakes a Cake’ provide the stimulus for the questions. Contents - A range of questions/instructions represent all four levels of Blank’s model. This screener offers two questions/instructions at each level for each picture presented. Space is provided beneath these questions for the clinician/teacher to transcribe the child’s response. It is not necessary to ask every question and many children would be unable to sustain interest if all questions were posed. The questions have been arranged into two sets to ensure that a variety of question types is included in each set. For screening purposes, one set is highlighted on the test form. It is recommended that you ask only one set of questions as each set of questions will ensure that you gain a functional picture of a child’s level of understanding. This simple screening tool can be used to plan goals for children and will monitor a child’s progress over time. On completion of the screener, the clinician or teacher enters the raw score of the number of questions asked at each level and the number of correct responses. The number correct at each level is then calculated as a percentage. The criteria referred to in this screener are provided by Marion Blank et al in the following publications ... • The Language of Learning: The Preschool Years - Blank, Rose & Berlin,1978 • Preschool Language Assessment Instrument (PLAI) - Blank, Rose, Berlin, Laura, 1978 Examples of questions provided in the screener: Level 3 Selecting an object by excluding a specific object Find something that is red but is not an apple. Selecting an alternative Sally is holding a cloth. Tell me something else that she could use to pick up the cake. Describing an event that might happen Sally is reading her shopping list. What will she do next? Defining a word What is an egg? Tell me what an egg is. Identifying Similarities This is a card and this is an envelope. How are these things the same? Generalising about a set of events (Point to the bones scattered on the table.) What happened to these bones? Citing an example by excluding a set of objects Tell me something that you can’t wear. -
 USING BOOKS TO ENHANCE A CHILD'S UNDERSTANDING AND INCREASE HIS/HER EXPRESSIVE LANGUAGE You can use a book to expand a child's • vocabulary (pond, fox, goat, windmill, jumped, stinging) • understanding of concepts (e.g. wet, heavy, light, white, many, through) • ability to understand questions Wise Words Scripts - offer clinicians, teachers and parents readily available questions designed specifically for each book. A script provides a variety of questions at each level of understanding for each page of the book. A teacher or clinician working with a group of children can tailor questions to each child's language ability. This script and other available scripts have been based on Marion Blank's Model of Classroom Language. Marion Blank recognised the importance of keeping questions and statements within a child’s level of understanding. The more concrete the statement or question, the easier it will be for the child to understand. As questions become more abstract, they become harder for children to answer. The Blank Model is divided into 4 levels of questioning, moving from the concrete (easiest) at Level 1 to the abstract (most difficult) at Level 4.
USING BOOKS TO ENHANCE A CHILD'S UNDERSTANDING AND INCREASE HIS/HER EXPRESSIVE LANGUAGE You can use a book to expand a child's • vocabulary (pond, fox, goat, windmill, jumped, stinging) • understanding of concepts (e.g. wet, heavy, light, white, many, through) • ability to understand questions Wise Words Scripts - offer clinicians, teachers and parents readily available questions designed specifically for each book. A script provides a variety of questions at each level of understanding for each page of the book. A teacher or clinician working with a group of children can tailor questions to each child's language ability. This script and other available scripts have been based on Marion Blank's Model of Classroom Language. Marion Blank recognised the importance of keeping questions and statements within a child’s level of understanding. The more concrete the statement or question, the easier it will be for the child to understand. As questions become more abstract, they become harder for children to answer. The Blank Model is divided into 4 levels of questioning, moving from the concrete (easiest) at Level 1 to the abstract (most difficult) at Level 4. -

Level 4
Explaining an inference “How can you tell that ...?” “How do you know that ...?” Explaining obstacles to an action “Why can’t the ...?” “Why won’t the ...?" Formulating a solution “What could she do ...?” “What should the ... do ...?” Justifying a prediction “What will happen if ...?” “Why can’t ...?” “Why shouldn’t ...?” Justifying a decision - based on essential and non-essential characteristics “If a ... were ... would it still be ...?” “If a ... were made of ... would it still be ...? Working through this program will improve your child’s verbal organisation. The program will allow your child to attend to and process information, whilst retrieving and comparing this information to past experiences. Your child will need to compare the new verbal information with information which has already been stored. Each scene will offer him/her the opportunity to develop an understanding of more abstract language. It will also improve his/her ability to ignore non-relevant material, yet retain the relevant features or information from each scene. This program will target- Inferential Reasoning - the ability to draw a conclusion based on the facts and previous experiences.
- Problem Solving - the ability to identify obstacles and then formulate a solution to a problem.
- Justifying a Prediction - the ability to explain why an event may take place and why certain actions or behaviours should be avoided.
- Justifying a Decision - based on essential and non-essential characteristics of an object.
- How can you tell that the boy is having a haircut?
- How do you know that the hairdresser hasn’t finished cutting his hair?
- How do you know that the boy is at the hairdresser?
- Why is the boy wearing a cape?
- Why does the boy need to go to the hairdresser?
- What should the hairdresser do after the boy leaves?
-
Sale!
 THE PIP & POSY TOTAL PACKAGE includes 9 books ... • Pip & Posy - The New Friend • Pip & Posy - The Snowy Day • Pip & Posy - The Little Puddle • Pip & Posy - The Bedtime Frog • Pip & Posy - The Big Balloon • Pip & Posy - The Scary Monster • Pip & Posy - The Super Scooter • Pip & Posy - The The Friendly Snail • Pip & Posy - The Christmas Tree These scripts have been based on Marion Blank's Model of Classroom Language. Marion Blank recognised the importance of keeping questions and statements within a child’s level of understanding. The more concrete the statement or question, the easier it will be for the child to understand. As questions become more abstract, they become harder for children to answer. The Blank Model is divided into 4 levels of questioning, moving from the concrete (easiest) at Level 1 to the abstract (most difficult) at Level 4.
THE PIP & POSY TOTAL PACKAGE includes 9 books ... • Pip & Posy - The New Friend • Pip & Posy - The Snowy Day • Pip & Posy - The Little Puddle • Pip & Posy - The Bedtime Frog • Pip & Posy - The Big Balloon • Pip & Posy - The Scary Monster • Pip & Posy - The Super Scooter • Pip & Posy - The The Friendly Snail • Pip & Posy - The Christmas Tree These scripts have been based on Marion Blank's Model of Classroom Language. Marion Blank recognised the importance of keeping questions and statements within a child’s level of understanding. The more concrete the statement or question, the easier it will be for the child to understand. As questions become more abstract, they become harder for children to answer. The Blank Model is divided into 4 levels of questioning, moving from the concrete (easiest) at Level 1 to the abstract (most difficult) at Level 4. -

Level 3
The Mind Map Advantage can be used to support a child to understand and answer questions. At the same time, this resource will increase a child’s expressive language. The Mind Map Advantage targets Level 3 of the Blank Model. At this level, a child is required to deal with questions that are more complex and subtle than at earlier levels. For example, the child is not dealing with immediate experiences, as the objects may or may not be present. In order to achieve a correct response, he must use language to restructure and reorder his experiences whilst attending to less prominent information. Although a child may understand the posed question, he may be unable to formulate a definition. This resource uses a fixed framework. It will support children ...- when defining words
- when answering questions
- when asking questions
- who have word-finding difficulties
-
 USING BOOKS TO ENHANCE A CHILD'S UNDERSTANDING AND INCREASE HIS/HER EXPRESSIVE LANGUAGE You can use a book to expand a child's • vocabulary (appeared, snatched, sore, tricks) • understanding of concepts (e.g. fast, easy, careful, soft) • ability to understand questions Wise Words Scripts - offer clinicians, teachers and parents readily available questions designed specifically for each book. A script provides a variety of questions at each level of understanding for each page of the book. A teacher or clinician working with a group of children can tailor questions to each child's language ability. This script and other available scripts have been based on Marion Blank's Model of Classroom Language. Marion Blank recognised the importance of keeping questions and statements within a child’s level of understanding. The more concrete the statement or question, the easier it will be for the child to understand. As questions become more abstract, they become harder for children to answer. The Blank Model is divided into 4 levels of questioning, moving from the concrete (easiest) at Level 1 to the abstract (most difficult) at Level 4.
USING BOOKS TO ENHANCE A CHILD'S UNDERSTANDING AND INCREASE HIS/HER EXPRESSIVE LANGUAGE You can use a book to expand a child's • vocabulary (appeared, snatched, sore, tricks) • understanding of concepts (e.g. fast, easy, careful, soft) • ability to understand questions Wise Words Scripts - offer clinicians, teachers and parents readily available questions designed specifically for each book. A script provides a variety of questions at each level of understanding for each page of the book. A teacher or clinician working with a group of children can tailor questions to each child's language ability. This script and other available scripts have been based on Marion Blank's Model of Classroom Language. Marion Blank recognised the importance of keeping questions and statements within a child’s level of understanding. The more concrete the statement or question, the easier it will be for the child to understand. As questions become more abstract, they become harder for children to answer. The Blank Model is divided into 4 levels of questioning, moving from the concrete (easiest) at Level 1 to the abstract (most difficult) at Level 4. -
 USING BOOKS TO ENHANCE A CHILD'S UNDERSTANDING AND INCREASE HIS/HER EXPRESSIVE LANGUAGE You can use a book to expand a child's • Vocabulary (magnificent, sail, squelchy, sniffing, pretending) • Understanding of concepts (e.g. cold, round, white, cosy, kind, sometimes) • Ability to understand questions Wise Words Scripts - offer clinicians, teachers and parents readily available questions designed specifically for each book. A script provides a variety of questions at each level of understanding for each page of the book. A teacher or clinician working with a group of children can tailor questions to each child's language ability. This script and other available scripts have been based on Marion Blank's Model of Classroom Language. Marion Blank recognised the importance of keeping questions and statements within a child’s level of understanding. The more concrete the statement or question, the easier it will be for the child to understand. As questions become more abstract, they become harder for children to answer. The Blank Model is divided into 4 levels of questioning, moving from the concrete (easiest) at Level 1 to the abstract (most difficult) at Level 4.
USING BOOKS TO ENHANCE A CHILD'S UNDERSTANDING AND INCREASE HIS/HER EXPRESSIVE LANGUAGE You can use a book to expand a child's • Vocabulary (magnificent, sail, squelchy, sniffing, pretending) • Understanding of concepts (e.g. cold, round, white, cosy, kind, sometimes) • Ability to understand questions Wise Words Scripts - offer clinicians, teachers and parents readily available questions designed specifically for each book. A script provides a variety of questions at each level of understanding for each page of the book. A teacher or clinician working with a group of children can tailor questions to each child's language ability. This script and other available scripts have been based on Marion Blank's Model of Classroom Language. Marion Blank recognised the importance of keeping questions and statements within a child’s level of understanding. The more concrete the statement or question, the easier it will be for the child to understand. As questions become more abstract, they become harder for children to answer. The Blank Model is divided into 4 levels of questioning, moving from the concrete (easiest) at Level 1 to the abstract (most difficult) at Level 4. -
 USING BOOKS TO ENHANCE A CHILD'S UNDERSTANDING AND INCREASE HIS/HER EXPRESSIVE LANGUAGE You can use a book to expand a child's • Vocabulary (stool, kennel, basket, sty, reaching, searching) • Understanding of concepts (e.g. big - little, wet - dry, nearly, scary, funny) • Ability to understand questions Wise Words Scripts - offer clinicians, teachers and parents readily available questions designed specifically for each book. A script provides a variety of questions at each level of understanding for each page of the book. A teacher or clinician working with a group of children can tailor questions to each child's language ability. This script and other available scripts have been based on Marion Blank's Model of Classroom Language. Marion Blank recognised the importance of keeping questions and statements within a child’s level of understanding. The more concrete the statement or question, the easier it will be for the child to understand. As questions become more abstract, they become harder for children to answer. The Blank Model is divided into 4 levels of questioning, moving from the concrete (easiest) at Level 1 to the abstract (most difficult) at Level 4.
USING BOOKS TO ENHANCE A CHILD'S UNDERSTANDING AND INCREASE HIS/HER EXPRESSIVE LANGUAGE You can use a book to expand a child's • Vocabulary (stool, kennel, basket, sty, reaching, searching) • Understanding of concepts (e.g. big - little, wet - dry, nearly, scary, funny) • Ability to understand questions Wise Words Scripts - offer clinicians, teachers and parents readily available questions designed specifically for each book. A script provides a variety of questions at each level of understanding for each page of the book. A teacher or clinician working with a group of children can tailor questions to each child's language ability. This script and other available scripts have been based on Marion Blank's Model of Classroom Language. Marion Blank recognised the importance of keeping questions and statements within a child’s level of understanding. The more concrete the statement or question, the easier it will be for the child to understand. As questions become more abstract, they become harder for children to answer. The Blank Model is divided into 4 levels of questioning, moving from the concrete (easiest) at Level 1 to the abstract (most difficult) at Level 4. -
Vowel 'ir' Minimal Pairs
Using Contrastive Pairs This program uses the contrastive phonological approach of Minimal Pairs. The use of minimal pairs is supported by evidence based practice and has been shown to be an effective and efficient treatment for contrasting vowels or consonants. The minimal pair approach - Although many children progress quickly through a vowel articulation program, some children respond more quickly using a phonological approach. The minimal pair approach involves single contrastive pairings of the child’s error with the target sound. In this program the vowel ‘ir’ is contrasted with ‘or’ which most typically replaces ‘ir’. As vocabulary restrictions prevent minimal pair practice at the CV (consonant-vowel) or VC (vowel-consonant) level, it is necessary to use CVC (consonant-vowel-consonant) words as minimal pairs. It is recommended that some ‘ir’ words are not targeted in practice. This group of words should be retained as a probe for generalisation. -
Sale!
 10% Discount Applied to Total Scripts Package (See individual programs for details and examples.) The Total Scripts Package includes 31 scripts: Sneezy the Snowman Rosie's Walk Smelly Socks Belinda The Gruffalo The Gruffalo's Child Stick Man The Smartest Giant in Town Room on the Broom A Squash and a Squeeze Pip & Posy - The Little Puddle Pip & Posy - The Friendly Snail Pip & Posy - The New Friend Pip & Posy - The Christmas Tree Pip & Posy - The Scary Monster Pip & Posy - The Bedtime Frog Pip & Posy - The Big Balloon Pip & Posy - The Snowy Day Pip & Posy - The Super Scooter Where's Spot? Spot Goes to the Park Spot Bakes a Cake Spot Goes to the Circus Spot Goes to School Spot Goes to a Party Spot Goes to the Farm Spot's Birthday Party Spot Visits his Grandparents Spot's Baby Sister Spot Stay's Overnight Spot Goes on Holiday Spot's First Easter USING BOOKS TO HELP YOUR CHILD UNDERSTAND QUESTIONS You can use books to expand your child's • Vocabulary (branch, shivered, paddock, melt, disguise, wind, poisonous, squelchy) • Understanding of concepts (warm, favourite, enormous, kind ) • Ability to understand questions Wise Words Scripts - offer clinicians, teachers and parents readily available questions designed specifically for each book. These scripts have been based on Marion Blank's Model of Classroom Language. Marion Blank recognised the importance of keeping questions and statements within a child’s level of understanding. The more concrete the statement or question, the easier it will be for the child to understand. As questions become more abstract, they become harder for children to answer. The Blank Model is divided into 4 levels of questioning, moving from the concrete (easiest) at Level 1 to the abstract (most difficult) at Level 4.
10% Discount Applied to Total Scripts Package (See individual programs for details and examples.) The Total Scripts Package includes 31 scripts: Sneezy the Snowman Rosie's Walk Smelly Socks Belinda The Gruffalo The Gruffalo's Child Stick Man The Smartest Giant in Town Room on the Broom A Squash and a Squeeze Pip & Posy - The Little Puddle Pip & Posy - The Friendly Snail Pip & Posy - The New Friend Pip & Posy - The Christmas Tree Pip & Posy - The Scary Monster Pip & Posy - The Bedtime Frog Pip & Posy - The Big Balloon Pip & Posy - The Snowy Day Pip & Posy - The Super Scooter Where's Spot? Spot Goes to the Park Spot Bakes a Cake Spot Goes to the Circus Spot Goes to School Spot Goes to a Party Spot Goes to the Farm Spot's Birthday Party Spot Visits his Grandparents Spot's Baby Sister Spot Stay's Overnight Spot Goes on Holiday Spot's First Easter USING BOOKS TO HELP YOUR CHILD UNDERSTAND QUESTIONS You can use books to expand your child's • Vocabulary (branch, shivered, paddock, melt, disguise, wind, poisonous, squelchy) • Understanding of concepts (warm, favourite, enormous, kind ) • Ability to understand questions Wise Words Scripts - offer clinicians, teachers and parents readily available questions designed specifically for each book. These scripts have been based on Marion Blank's Model of Classroom Language. Marion Blank recognised the importance of keeping questions and statements within a child’s level of understanding. The more concrete the statement or question, the easier it will be for the child to understand. As questions become more abstract, they become harder for children to answer. The Blank Model is divided into 4 levels of questioning, moving from the concrete (easiest) at Level 1 to the abstract (most difficult) at Level 4. -
 USING BOOKS TO ENHANCE A CHILD'S UNDERSTANDING AND INCREASE HIS/HER EXPRESSIVE LANGUAGE You can use a book to expand a child's • vocabulary (honey, clock, piano, hippo, eating, racing, basket, rug) • understanding of concepts (e.g. empty, hungry, under, in, naughty) • ability to understand questions Wise Words Scripts - offer clinicians, teachers and parents readily available questions designed specifically for each book. A script provides a variety of questions at each level of understanding for each page of the book. A teacher or clinician working with a group of children can tailor questions to each child's language ability. This script and other available scripts have been based on Marion Blank's Model of Classroom Language. Marion Blank recognised the importance of keeping questions and statements within a child’s level of understanding. The more concrete the statement or question, the easier it will be for the child to understand. As questions become more abstract, they become harder for children to answer. The Blank Model is divided into 4 levels of questioning, moving from the concrete (easiest) at Level 1 to the abstract (most difficult) at Level 4.
USING BOOKS TO ENHANCE A CHILD'S UNDERSTANDING AND INCREASE HIS/HER EXPRESSIVE LANGUAGE You can use a book to expand a child's • vocabulary (honey, clock, piano, hippo, eating, racing, basket, rug) • understanding of concepts (e.g. empty, hungry, under, in, naughty) • ability to understand questions Wise Words Scripts - offer clinicians, teachers and parents readily available questions designed specifically for each book. A script provides a variety of questions at each level of understanding for each page of the book. A teacher or clinician working with a group of children can tailor questions to each child's language ability. This script and other available scripts have been based on Marion Blank's Model of Classroom Language. Marion Blank recognised the importance of keeping questions and statements within a child’s level of understanding. The more concrete the statement or question, the easier it will be for the child to understand. As questions become more abstract, they become harder for children to answer. The Blank Model is divided into 4 levels of questioning, moving from the concrete (easiest) at Level 1 to the abstract (most difficult) at Level 4. -
 USING BOOKS TO ENHANCE A CHILD'S UNDERSTANDING AND INCREASE HIS/HER EXPRESSIVE LANGUAGE You can use a book to expand a child's • Vocabulary (stool, kennel, basket, sty, reaching, searching) • Understanding of concepts (e.g. big - little, wet - dry, nearly, scary, funny) • Ability to understand questions Wise Words Scripts - offer clinicians, teachers and parents readily available questions designed specifically for each book. A script provides a variety of questions at each level of understanding for each page of the book. A teacher or clinician working with a group of children can tailor questions to each child's language ability. This script and other available scripts have been based on Marion Blank's Model of Classroom Language. Marion Blank recognised the importance of keeping questions and statements within a child’s level of understanding. The more concrete the statement or question, the easier it will be for the child to understand. As questions become more abstract, they become harder for children to answer. The Blank Model is divided into 4 levels of questioning, moving from the concrete (easiest) at Level 1 to the abstract (most difficult) at Level 4.
USING BOOKS TO ENHANCE A CHILD'S UNDERSTANDING AND INCREASE HIS/HER EXPRESSIVE LANGUAGE You can use a book to expand a child's • Vocabulary (stool, kennel, basket, sty, reaching, searching) • Understanding of concepts (e.g. big - little, wet - dry, nearly, scary, funny) • Ability to understand questions Wise Words Scripts - offer clinicians, teachers and parents readily available questions designed specifically for each book. A script provides a variety of questions at each level of understanding for each page of the book. A teacher or clinician working with a group of children can tailor questions to each child's language ability. This script and other available scripts have been based on Marion Blank's Model of Classroom Language. Marion Blank recognised the importance of keeping questions and statements within a child’s level of understanding. The more concrete the statement or question, the easier it will be for the child to understand. As questions become more abstract, they become harder for children to answer. The Blank Model is divided into 4 levels of questioning, moving from the concrete (easiest) at Level 1 to the abstract (most difficult) at Level 4. -
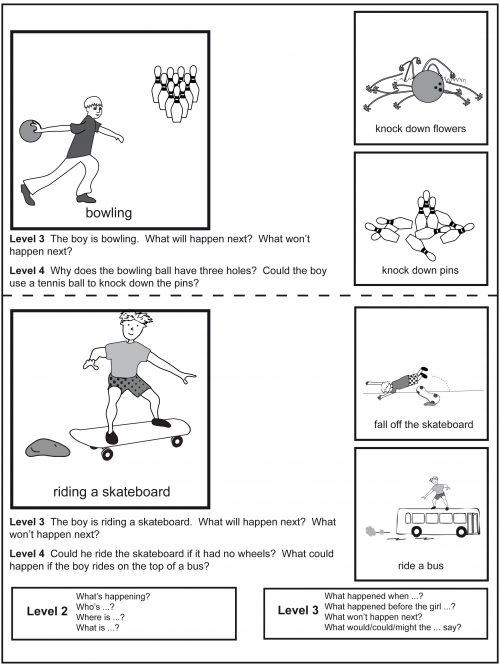
Level 3
Describing an event that might happen Level 3 “What might happen next?” “What will happen next?” “What could happen next?” Describing an event that won't happen Level 3 “What won't happen next?" "What won't the boy do next?" Reasoning, justifying and predicting Level 4 “Would a bowling ball be a bowling ball if it were made of cotton wool?” “How could the boy avoid falling off his skateboard?” “Why shouldn't the boy ride on top of the bus?” Contents - Learning to sequence is an important language component for your child. This program will help your child understand and express ordinal and causal relationships. He/she will require sequencing skills to create narratives as his/her language develops. The ability to sequence an event will help your child to organise information and ideas with greater efficiency. As you help your child to sequence stories, this program will also reinforce a number of concepts (first, last, before, after). Working through the program will serve as an early step in developing your child's ability to produce a story. Example of a task/activity Cover the two smaller pictures on the right and ask your child to describe what is happening in the large picture on the left. If your child is unable to describe the event occurring in the large picture, you should model the complete sentence for him/her. "The boy is buying a cake." Next, cover the large picture and uncover the two smaller pictures. Point to each small picture as you ask "What's happening?" or "What happened ...?" Encourage your child to describe what is happening in each picture. Again you should describe the event/s in the picture for your child if he/she is unable to do so. Now uncover all three pictures and ask either "What will happen next?" or "What won't happen next?" To further extend this activity you may wish to ask additional questions such as... "What happened before ...? What happened after...? What happened first?" As a final task you may wish to cover all the pictures in the sequence and point to the left side of the page asking "Tell me the story. Tell me what happened." (You may need to prompt your child with "next ..." and "then ...") -
 USING BOOKS TO ENHANCE A CHILD'S UNDERSTANDING AND INCREASE HIS/HER EXPRESSIVE LANGUAGE You can use a book to expand a child's • vocabulary (snow, waterproof, mittens, snowflakes, sorry, footprints) • understanding of concepts (e.g. warm, comfy, cold, kind) • ability to understand questions Wise Words Scripts - offer clinicians, teachers and parents readily available questions designed specifically for each book. A script provides a variety of questions at each level of understanding for each page of the book. A teacher or clinician working with a group of children can tailor questions to each child's language ability. This script and other available scripts have been based on Marion Blank's Model of Classroom Language. Marion Blank recognised the importance of keeping questions and statements within a child’s level of understanding. The more concrete the statement or question, the easier it will be for the child to understand. As questions become more abstract, they become harder for children to answer. The Blank Model is divided into 4 levels of questioning, moving from the concrete (easiest) at Level 1 to the abstract (most difficult) at Level 4.
USING BOOKS TO ENHANCE A CHILD'S UNDERSTANDING AND INCREASE HIS/HER EXPRESSIVE LANGUAGE You can use a book to expand a child's • vocabulary (snow, waterproof, mittens, snowflakes, sorry, footprints) • understanding of concepts (e.g. warm, comfy, cold, kind) • ability to understand questions Wise Words Scripts - offer clinicians, teachers and parents readily available questions designed specifically for each book. A script provides a variety of questions at each level of understanding for each page of the book. A teacher or clinician working with a group of children can tailor questions to each child's language ability. This script and other available scripts have been based on Marion Blank's Model of Classroom Language. Marion Blank recognised the importance of keeping questions and statements within a child’s level of understanding. The more concrete the statement or question, the easier it will be for the child to understand. As questions become more abstract, they become harder for children to answer. The Blank Model is divided into 4 levels of questioning, moving from the concrete (easiest) at Level 1 to the abstract (most difficult) at Level 4. -
 Wise Words indigenous materials have been devised to support parents, teachers and clinicians who may find it challenging to teach indigenous content because of concerns that they may not have the knowledge or understanding to ensure that the books, their stories and the complexity of the information is presented in a respectful and appropriate manner. With thanks to Tara Lewis who kindly edited these resources. Tara Lewis is a Speech Pathologist and member of Speech Pathology Australia's Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander Advisory Committee. Tara is an Iman woman from the Taroom country of Western Queensland. The Australian Curriculum has established Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander histories and cultures as a priority. This will ensure that Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander students are able to see themselves, their identities and their cultures reflected in the curriculum of each of the learning areas. Exposure to these and other indigenous books can build awareness of and respect for Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander histories and cultures amongst all Australian children. USING BOOKS TO ENHANCE A CHILD'S UNDERSTANDING AND INCREASE HIS/HER EXPRESSIVE LANGUAGE You can use a book to expand a child's • Vocabulary (galaxy, mudskippers, feathers, tide, goanna) • Understanding of concepts (e.g. lucky, fresh, silly, first) • Ability to understand questions Two Mates is the true story of the special friendship between two young boys who have grown up together in the coastal town of Broome in Australia's north-west. The book describes their lives and how each boy recognises the special talents of each other. Jack is Aboriginal and Raf is a non-Aboriginal boy who has spina bifida. Wise Words Scripts - offer clinicians, teachers and parents readily available questions designed specifically for each book. A script provides a variety of questions at each level of understanding for each page of the book. A teacher or clinician working with a group of children can tailor questions to each child's language ability. This script and other available scripts have been based on Marion Blank's Model of Classroom Language.
Wise Words indigenous materials have been devised to support parents, teachers and clinicians who may find it challenging to teach indigenous content because of concerns that they may not have the knowledge or understanding to ensure that the books, their stories and the complexity of the information is presented in a respectful and appropriate manner. With thanks to Tara Lewis who kindly edited these resources. Tara Lewis is a Speech Pathologist and member of Speech Pathology Australia's Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander Advisory Committee. Tara is an Iman woman from the Taroom country of Western Queensland. The Australian Curriculum has established Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander histories and cultures as a priority. This will ensure that Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander students are able to see themselves, their identities and their cultures reflected in the curriculum of each of the learning areas. Exposure to these and other indigenous books can build awareness of and respect for Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander histories and cultures amongst all Australian children. USING BOOKS TO ENHANCE A CHILD'S UNDERSTANDING AND INCREASE HIS/HER EXPRESSIVE LANGUAGE You can use a book to expand a child's • Vocabulary (galaxy, mudskippers, feathers, tide, goanna) • Understanding of concepts (e.g. lucky, fresh, silly, first) • Ability to understand questions Two Mates is the true story of the special friendship between two young boys who have grown up together in the coastal town of Broome in Australia's north-west. The book describes their lives and how each boy recognises the special talents of each other. Jack is Aboriginal and Raf is a non-Aboriginal boy who has spina bifida. Wise Words Scripts - offer clinicians, teachers and parents readily available questions designed specifically for each book. A script provides a variety of questions at each level of understanding for each page of the book. A teacher or clinician working with a group of children can tailor questions to each child's language ability. This script and other available scripts have been based on Marion Blank's Model of Classroom Language.
